 +86 152 6060 5085
+86 152 6060 5085
 +86 152 6060 5085
+86 152 6060 5085
Blog
Catalog
Latest Blog
✔ seam slippage - constant slippage test methods:
ASTM D 434-1995(this standard has been replaced, but still used habitually by many foreign buyers)
ASTM D1683 (used in place of ASTM d434-95 for determination of joint strength, joint slip, tensile strength, etc.)
ISO - 2004-13936.1
GB/T 13772.1 2008
JIS l1096-2010 section 8.23 method C
✔ slip test basic flow:
Sample humidity control = "sampling =" sample preparation = "equipment adjustment =" test = "result analysis
Sample humidity control: the sample should be humidity controlled for at least 4 hours in the standard atmospheric pressure environment (temperature 20℃, humidity 65%), and the sample with high moisture return should be humidity controlled for longer time.
Sampling: due to the diversity of fabrics, sampling should be representative. For example, jacquard fabrics should be processed according to the jacquard situation, whether the seam slip test of jacquard part and ground tissue part should be tested or not.For pigment printing weave, need to consider whether to avoid printing parts.
Sample making: in the process of sample making, it is necessary to make samples strictly according to the sample making methods and requirements stipulated by the content of each standard.
Equipment regulation: due to the difference of Seam slip tester produced by different equipment manufacturers at home and abroad, please carefully understand the equipment state (effective clamping area of clamping piece, clamping pressure of pneumatic fixture, sensitivity when the equipment stops drawing) and parameter setting (effective clamping distance and stretching rate) before the test.Whether the data collection mode and frequency of the equipment software meet the standard requirements.
Testing: during testing, testers are required to observe the sample testing process;To understand the abnormal phenomenon of samples in the test process;Instead of staring at a computer screen and stretching the curve.
Result analysis: not all test results are reasonable;We need to reject the test sample data with abnormal conditions and understand the fracture situation of each sample during the test, so as to analyze whether the test results meet the standard requirements.
Material preparation
Sewing needles:
The commonly used sewing needles for seam slippage of fabrics used in clothing are divided into no. 14 and no. 11 stitches.Different size and diameter of the needle will affect the size of the hole left in the fabric.This has a great influence on the constant load test, so we must pay attention to it.
The sharpness of the sewing needle will also affect the sewing damage rate of the fabric, thus affecting the maximum peak value of the fabric's seam strength, which is the main content of the seam slip.
Sewing thread:
Its main influence factor is its own strength, for ISO GB and other series of standards;The strength of sewing thread can meet the requirement of ≥200N, but for ASTM standard;The requirement is not ≥200N to stop the test;Instead, the actual joint slip value of the sample is required to be directly tested.In contrast, ASTM standards must be strictly adhered to the standard of sewing thread (ASTM D434 about 39 Tex white meringerized cotton thread or about 36 Tex white terylene thread, ASTM D1683 according to the type of fabric and the weight of the fabric - see table 1 in the standard).
Test direction problem
The testing direction is generally divided into two types
1. Meridional slip refers to the slip of weft on warp, corresponding to ASTM D434 and ASTM D1683
2. Meridional slip refers to the slip of warp yarn on weft, corresponding to GB/T 13772.1 and ISO 13936.1
The two are opposite, so when we get the test report, we must see which direction the yarn slip is bad.This is also sometimes difficult for customers to understand a problem.In order to be clear to the customers, each testing center has adopted the following result representation method.
// to warp
// to weft
It means that the suture is parallel to the meridian, and the suture is parallel to the latitudinal direction.
Notes for sample preparation
1. Except that JIS L1096 requires the sewing thread to be perpendicular to the warp (latitude), all other standards require the sewing thread to be parallel to the short side of the sample.
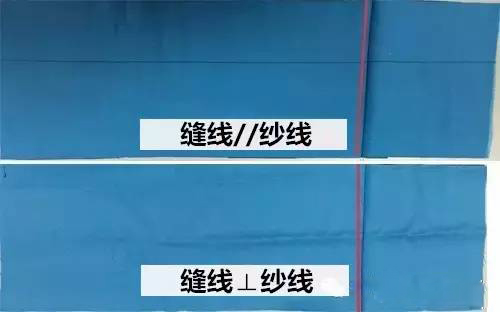
2. In addition to JIS L1096, other standards require drawing a straight line parallel to the long side at a distance of 38mm from the long side, so that the fixture can hold the same bundle of yarn during the test.(pictured above)
3. When sewing samples, be sure to check whether the tension between the upper and lower threads of the sewing machine is consistent.The diagram below:

If the sewing tension of the upper and lower thread is consistent, the sewn sample shall be evenly distributed on both sides.During the test, the tension of the yarn is uniform and can fully reflect the true stress of the sample.

As shown in the figure above, the tension of the upper and lower sewing thread is inconsistent. In this case, the tension strength of the sewing thread is relatively weak, and the test result is unstable.After several tests, it is found that the test result is slightly lower than the normal test value, and it is easy for the seam to break.
Solutions:
When the tension of the above sewing thread < the bottom line tension, the tension of the spring string holder on the sewing machine should be adjusted to increase the tension of the thread.Or adjust the second screw on the bottom line coil to use less tension.
When upper sewing thread tension > bottom line tension, reverse adjust as above method.
Email: hello@utstesters.com
Direct: + 86 152 6060 5085
Tel: +86-596-7686689
Web: www.utstesters.com