 +86 152 6060 5085
+86 152 6060 5085
 +86 152 6060 5085
+86 152 6060 5085
Blog
Catalog
Latest Blog
In daily life, we must often be troubled by various stains. If you happen to be wearing a white T-shirt, it can be devastating! Or, on a rainy day, you're walking by the side of the road and a car flies by, splashing mud all over you.
All kinds of awkwardness, what's the solution?
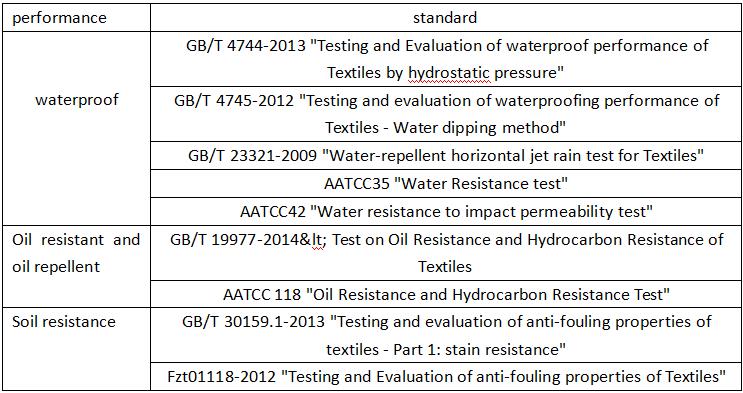
"Three prevention" clothing to escort you, with the development of society and the progress of science and technology, waterproof, oil, anti-fouling performance (commonly known as "three prevention") textiles have been developed by experts and scholars. Here, it is necessary to explain the definition of "three defenses".
Water resistance: The ability of fabric to prevent water from wetting or penetrating.
Oil resistance: Ability of fabric to resist absorption of oily liquids.
Antifouling: the performance of the material to resist contamination, that is, the material is not easy to adhere to dirt, or even if stained with the performance of clothing removal, to be resistant to contamination and easy to decontamination characterization.
"Three prevention" principle
1 wettability
Wetting refers to the process by which one liquid or gaseous substance on a solid surface is replaced by another liquid or gas. Wetting behavior can be seen everywhere in our daily life, such as water spread on cloth, rapeseed oil rolling on the bottom of the iron pot. The hydrophobic characteristics are due to the clever combination of special morphological and structural characteristics of low surface energy and micro/nano double scale roughness. It is generally believed that in the process of wetting behavior, when the surface tension of the substrate is constant, the larger the roughness is, the easier it is to be wetted, and vice versa.
2 contact Angle
The surface tension can be measured by the contact Angle (also known as the wetting Angle), which is the Angle θ between the gaseous and liquid interfaces and the solid (i.e. the fabric surface) and liquid interfaces. It can also be used as an important data to determine the hydrophobic properties of the substrate surface. When A water droplet falls on an infinitely smooth solid surface and reaches A state of rest, it is simultaneously affected by the interfacial tension γS/A between liquid and gas, the interfacial tension γS/L between solid and liquid, and the interfacial tension γS/A between solid and gas.
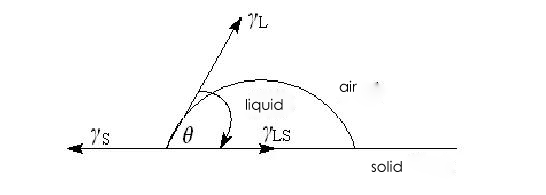
Young's equation can be used to describe the correlation between contact Angle θ and interfacial tension:
γS/A=γS/L+γL/A cosθ
cosθ=(γS/A -γS/L)/γL/A
Looking for Digital Hydrostatic Head Tester? Learn more info about our laboratory textile
testing machines here.
Email: hello@utstesters.com
Direct: + 86 152 6060 5085
Tel: +86-596-7686689
Web: www.utstesters.com