 +86 152 6060 5085
+86 152 6060 5085
 +86 152 6060 5085
+86 152 6060 5085
Blog
Catalog
Latest Blog
Twisting is to make the two sections of the yarn produce relative rotation, then the yarn in the original parallel to the yarn axis of the fiber tilt into a spiral line.For staple fibers, the main purpose of twisting is to increase yarn strength.The twisting of filament yarn can not only improve the strength of yarn, but also produce some effect.The amount of yarn twisting and the combination of twist direction and twist degree in the fabric have great influence on the appearance and properties of the product.
The indexes of twisting properties are:
1. Twist and twist coefficient representing twist degree
2. Twist direction of twisting direction.
1. The twist:
1. Twist: The number of twists per unit length of yarn.Yarn twist Angle twist one turn into one twist back.
Ttex- Special twist (twist /10cm, cotton yarn)
Tm metric twist (twist /m, worsted yarn and chemical filament)
Te -- English twist (twist per inch)
1 inch =2.54cm Ttex= 0.1tm = 3.937te
Method for measuring twist
There are two common twist testing methods in China: direct counting method and untwisting twisting method.The direct counting method is generally used in the test of staple fiber and twine, and the untwisting and twisting method is used in the test of spun yarn. In addition, there are two and three untwisting and sliding method.
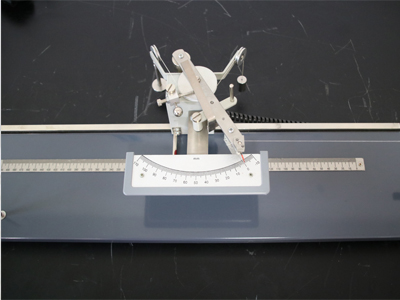
1 Direct counting method
Under a certain tension, the two ends of the yarn of known length are clamped, one end is fixed, and the other end rotates axially according to the untwisting direction until the single yarn in the strand or single yarn or single fiber in the complex filament is completely parallel. The receding twist number is the number of twists in the length of the yarn sample。
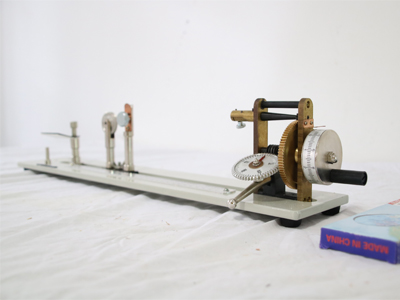
2 Untwist twist method
Under a certain tension, the two ends of the known yarn length are clamped, one end is fixed, and the other end is rotated axially in the direction of untwisting. The number of twists after untwisting and reverse twisting is measured, which is twice the number of twists within the length of the yarn sample.
Twist affects yarn strength, rigidity, flexibility, elasticity and shrinkage.As the twist increases, the strength of the yarn increases. However, the twist must not exceed a certain value, or the strength will decrease. This value is called the critical twist of the yarn.The critical twist of yarns of different materials is different.Generally, under the premise of meeting the requirements of strength, the smaller the twist, the better, because the increase of twist will make the yarn feel hard, elastic decline, shrinkage increases, which is also the reason why filament yarn is generally not twisted or less twisted.
In addition, the twist has an effect on the volume weight and diameter of the yarn, and the twisting effect increases the tightness of the yarn.In a certain range, the volume weight of the yarn increases with the increase of twist, and the diameter of the yarn decreases with the increase of twist, so that the covering and comfort of the fabric changes.
The twist should be selected according to the different fabric uses.
1.The warp yarn needs to have a high strength and a large twist;
2.The weft and knitting yarn should be soft and the twist should be small;
3.The yarn used for knitting and knitting fleece fabrics should have a small twist to facilitate fleece.
4.Thin crepe fabric, with smooth, stiff, cool characteristics, yarn twist should be larger.

2. Twist factor
The twist cannot be used to compare the twisting of yarns of different thicknesses, because the fibres of thick yarns tilt more than those of thin yarns with the same twist.In practical production, twist coefficient is often used to indicate the twisting degree of yarn.
The twist factor is calculated according to the twist and linear density of the yarn.
Twist coefficient is the relative value of yarn twisting degree combined with linear density, which can be used to compare the twisting degree of yarns of different thicknesses.The larger the value, the greater the twist.
The choice of twist factor: mainly depends on the nature of the material and the use of yarn.
1. When spinning with slender fibers, the twist factor of the yarn can be lower
2. When spinning with staple fiber, the twist factor should be higher
3. Warp yarn needs higher strength and higher twist coefficient
4. Weft and knitting yarn generally require soft, low twist coefficient
5. The yarn used for knitting and knitting should have a small twist coefficient to facilitate the fleece
6. Thin fabrics and knitted outerwear fabrics should have a smooth and cool style, and the yarn twist coefficient should be larger
7. Yarn fineness is different, twist coefficient is different, fine yarn twist coefficient should be larger
In general, the roving twist coefficient of chemical fiber is lower than that of pure cotton. When spinning cotton type chemical fiber, it is 50% ~ 60% of that of pure cotton, and when spinning medium length chemical fiber, it is about 40% ~ 50% of that of pure cotton. The specific data depends on the type and quantity of raw materials.
The twist coefficient of conventional yarn is as follows: ring spinning machine yarn 360-400;Ring spinning knitting yarn 320-360;Ring spinning low count flocking yarn 280-320;Air spinning, 400-440.
3. Lay
Twist direction refers to the inclination of the fiber in a single yarn or the single yarn in a twine.It is divided into Z twist and S twist two.After twisting, the yarn twist from the lower right corner to the upper left corner, tilt direction and the middle of "S" consistent called S twist or smooth twist;The yarn twist is tilted from the bottom left to the top right, and the tilt is consistent with the middle of the "Z", called the Z twist or backhand twist.Single yarn usually uses Z twist and twine uses S twist.
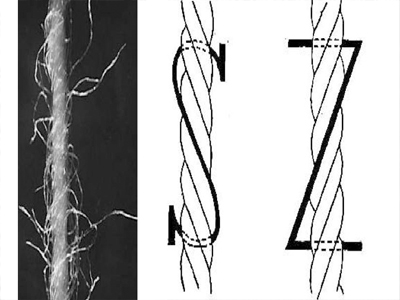
The twist of the twine according to the twist of the twist has always indicated.For example, single yarn with Z twist, initial twist with S twist, and double twist with Z twist, its twist direction is represented by ZSZ.
The twist direction of the yarn has a great influence on the appearance and feel of the fabric. By combining the twist direction of the warp and weft yarn with the fabric structure, different fabrics with different appearance and feel can be woven.
Looking for sample dyeing machine? Learn more info about our laboratory Yarn testing machines here.
Email: hello@utstesters.com
Direct: + 86 152 6060 5085
Tel: +86-596-7686689
Web: www.utstesters.com